What is the ECS?
CBD interacts with a series of receptors in our bodies, known as the Endocannabinoid System (ECS). CBD is absorbed into your cells and reacts with the body's ECS, which in turn interacts with various receptors in the brain, organs, muscles, tissues, and nerves to help maintain homeostasis.
The ECS also influences the state of immunity and enables a feedback system for almost all neurological functions, and this relationship between CBD and the ECS potentially indicates that CBD may offer patients a myriad of wellness benefits.
Endocannabinoids
Endocannabinoids Vs. Phytocannabinoids
- Endogenous cannabinoids, which are molecules made by your body.
- Examples include:
- anandamide (AEA)
- 2-arachidonoylglyerol (2-AG)
- Enzymes also play a role in the ECS, breaking down the cannabinoids.
- The two big enzymes are FAAH, which breaks down anandamide, and MAGL, which breaks down 2-AG.
- Endogenous cannabinoids, which are molecules made by your body.
- Examples include:
- anandamide (AEA)
- 2-arachidonoylglyerol (2-AG)
- Enzymes also play a role in the ECS, breaking down the cannabinoids.
- The two big enzymes are FAAH, which breaks down anandamide, and MAGL, which breaks down 2-AG.

- Structurally diverse class of naturally occurring chemical constituents in the genus Cannabis
- The most abundant phytocannabinoids found in the cannabis plant are 6.9- tetrahydrocannabinol (THC) and cannabidiol (CBD).
- Other cannabinoid include THCA, CBDA, CBG, CBGA, CBC, CBCA, CBCV, CBCVA, CBDV, CBDVA, CBN
Phytocannabinoids
- Structurally diverse class of naturally occurring chemical constituents in the genus Cannabis
- The most abundant phytocannabinoids found in the cannabis plant are 6.9- tetrahydrocannabinol (THC) and cannabidiol (CBD).
- Other cannabinoid include THCA, CBDA, CBG, CBGA, CBC, CBCA, CBCV, CBCVA, CBDV, CBDVA, CBN

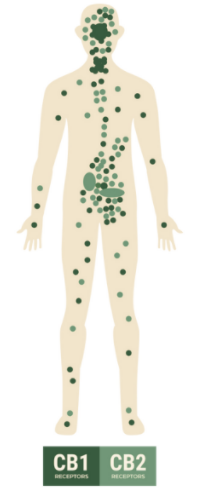
Types Of Receptors
CB1 - Brain, spinal cord, pituitary gland, adrenal gland, thyroid gland, fat cells, muscles cells, liver cells, digestive tract, lungs
CB2 - Brain, immune system, digestive tract, nerves
TRPV1 - Brain, bone marrow, muscles, liver, digestive tract, kidneys, bladder, reproductive system, fat cells
GPR18 - Bone marrow, immune system, reproductive system
GPRSS - Brain, bone marrow, immune system, reproductive system, bladder, intestines
GPR119 - Pancreas, digestive tract
What is CBD?
Cannabidiol is a Popular Natural Remedy Used For Many Common Ailments
Better known as CBD, it is one of more than 100 chemical compounds called cannabinoids that are found in the cannabis plant, Cannabis sativa.
Tetrahydrocannabinol (THC) is the main psychoactive cannabinoid found in cannabis, which means it causes the sensation of getting high that’s often associated with cannabis.
However, Unlike THC, CBD is Not Psychoactive.
This quality makes CBD an appealing option for those who are looking for relief from pain and other symptoms without the mind-altering effects of cannabis or other side effects related to some pharmaceutical drugs.
CBD oil is made by extracting CBD from the cannabis plant and then diluting it with a carrier oil like coconut oil or hemp seed oil. CBD can be found in a variety of products online and in stores, including dietary supplements, bath soaks, drinks, and food.
𝘐𝘵 𝘤𝘰𝘯𝘵𝘪𝘯𝘶𝘦𝘴 𝘵𝘰 𝘨𝘢𝘪𝘯 𝘮𝘰𝘮𝘦𝘯𝘵𝘶𝘮 𝘪𝘯 𝘵𝘩𝘦 𝘩𝘦𝘢𝘭𝘵𝘩 𝘢𝘯𝘥 𝘸𝘦𝘭𝘭𝘯𝘦𝘴𝘴 𝘸𝘰𝘳𝘭𝘥, 𝘸𝘪𝘵𝘩 𝘴𝘰𝘮𝘦 𝘴𝘤𝘪𝘦𝘯𝘵𝘪𝘧𝘪𝘤 𝘴𝘵𝘶𝘥𝘪𝘦𝘴 𝘧𝘪𝘯𝘥𝘪𝘯𝘨 𝘵𝘩𝘢𝘵 𝘪𝘵 𝘮𝘢𝘺 𝘦𝘢𝘴𝘦 𝘴𝘺𝘮𝘱𝘵𝘰𝘮𝘴 𝘰𝘧 𝘤𝘰𝘯𝘥𝘪𝘵𝘪𝘰𝘯𝘴 𝘴𝘶𝘤𝘩 𝘢𝘴 𝘤𝘩𝘳𝘰𝘯𝘪𝘤 𝘱𝘢𝘪𝘯 𝘢𝘯𝘥 𝘢𝘯𝘹𝘪𝘦𝘵𝘺.
MEDICAL DISCLAIMER
This content is for informational and educational purposes only. It is not intended to provide medical advice or to take the place of such advice or treatment from a personal physician. All readers/viewers of this content are advised to consult their doctors or qualified health professionals regarding specific health questions. Neither Cecilia Ahanonu, PA-C nor the publisher of this content takes responsibility for possible health consequences of any person or persons reading or following the information in this educational content. All viewers of this content, especially those taking prescription or over-the-counter medications, should consult their physicians before beginning any nutrition, supplement or lifestyle program.





